😊 Ready to master the art of writing in interval notation? This blog post will guide you through the process, step-by-step, with engaging paragraphs and helpful examples. Interval notation is a powerful tool in mathematics, enabling you to describe sets of numbers with precision and clarity. Whether you’re a student, a researcher, or simply someone curious about mathematics, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to write in interval notation like a pro.
Table of Contents
- What is Interval Notation?
- Understanding the Concept
- Different Types of Intervals
- How to Write in Interval Notation:
- Open and Closed Intervals
- Using Parentheses and Brackets
- Writing Infinite Intervals
- Examples of Interval Notation:
- Representing Various Sets of Numbers
- Properties of Intervals:
- Understanding Boundedness
- Exploring Length and Emptiness
- Comparison Table: Interval Notation vs. Other Notations
- Applications of Interval Notation:
- Describing Real-World Scenarios
- Conclusion
Source curvebreakerstestprep.com
Now, let’s dive into the exciting world of interval notation!
What is Interval Notation?
Interval notation is a concise way of representing sets of numbers on the number line. It uses mathematical symbols to define the boundaries of the set and to specify whether the endpoints are included or excluded. Understanding interval notation is crucial for working with inequalities, limits, and other advanced mathematical concepts.
Different Types of Intervals
There are three main types of intervals:
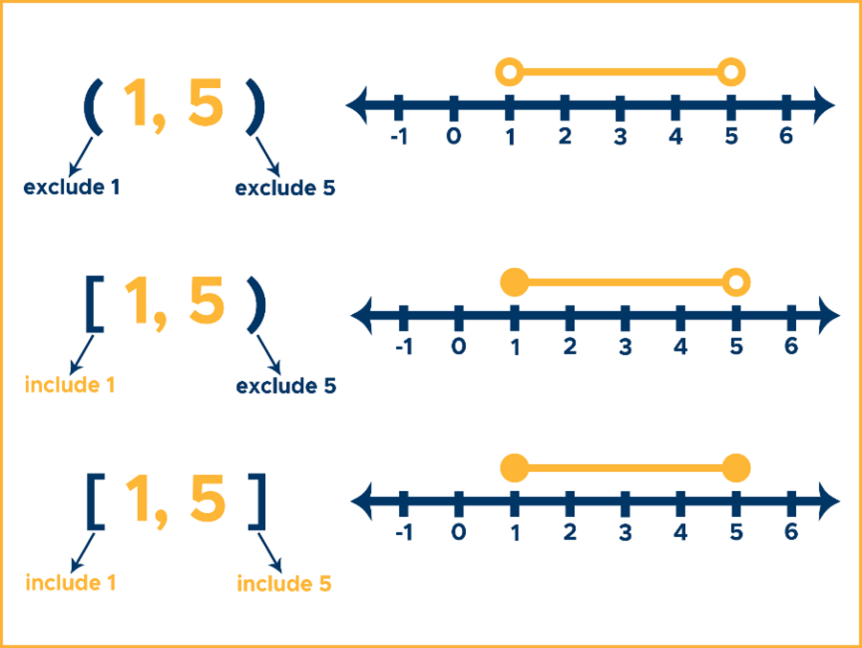
- Open Interval: Represented as (a, b), it includes all numbers between a and b but excludes the endpoints themselves.
- Closed Interval: Represented as [a, b], it includes all numbers between a and b as well as the endpoints themselves.
- Half-Open Interval: Represented as [a, b) or (a, b], it includes one endpoint but excludes the other.
How to Write in Interval Notation
Writing in interval notation is easy if you follow these simple rules:
Open and Closed Intervals
- Open Interval: (a, b)
- Example: (2, 5) represents all numbers greater than 2 and less than 5.
- Closed Interval: [a, b]
- Example: [2, 5] represents all numbers greater than or equal to 2 and less than or equal to 5.
Using Parentheses and Brackets
- Parentheses: Used to denote open intervals, indicating that the endpoints are excluded.
- Brackets: Used to denote closed intervals, indicating that the endpoints are included.
Writing Infinite Intervals
- Positive Infinity: Represented as ∞
- Example: [3, ∞) represents all numbers greater than or equal to 3.
- Negative Infinity: Represented as -∞
- Example: (-∞, 2] represents all numbers less than or equal to 2.
Examples of Interval Notation
Let’s explore some examples to solidify your understanding:
- (1, 3): Represents all numbers between 1 and 3, excluding the endpoints.
- [0, 10]: Represents all numbers between 0 and 10, including both endpoints.
- (-2, ∞): Represents all numbers greater than -2.
Properties of Intervals
Intervals possess certain properties that are essential to understand:
Boundedness
- Bounded Interval: Has both a lower and upper bound.
- Unbounded Interval: Has only one bound or no bounds at all.
Length and Emptiness
- Length of an Interval: Distance between the endpoints.
- Empty Interval: An interval with no numbers in it.
Comparison Table: Interval Notation vs. Other Notations
| Notation | Description |
|---|---|
| Interval Notation | Represents sets of numbers on the number line |
| Inequality Notation | Describes relationships between numbers |
| Set Builder Notation | Defines sets using mathematical rules |
Applications of Interval Notation
Interval notation finds wide application in mathematics, including:
- Describing ranges of functions
- Expressing solutions to inequalities
- Representing sets of data in statistics
- Modeling real-world scenarios, such as temperature ranges or time intervals
Conclusion
Congratulations! Now you have the knowledge and skills to write in interval notation with confidence. Whether you’re solving mathematical problems, analyzing data, or exploring advanced mathematical concepts, interval notation will be an invaluable tool in your toolkit.
If you enjoyed this guide, be sure to check out our other articles on related topics, such as:
- A Beginner’s Guide to Algebraic Expressions
- Mastering the Art of Simplifying Radicals
- Unlocking the Secrets of Exponents
Your feedback is always welcome! Please feel free to comment below with any questions, suggestions, or experiences you’d like to share. Happy number-crunching!
FAQ about Interval Notation
1. What is interval notation?
It is a mathematical way to describe the distance between two notes.
2. What are the three guidelines for writing interval notation (P-A-S)?
- P: The interval’s "Perfect," "Augmented," or "Diminished" quality
- A: The interval’s "Alteration" (if any)
- S: The interval’s "Size"
3. What does the "P" stand for?
The "Perfect," "Augmented," or "Diminished" quality of the interval.
4. What does the "A" stand for?
The "Alteration" (if any), such as sharp (#), flat (b), or natural (n).
5. What does the "S" stand for?
The interval’s "Size," which is measured in half steps (or semitones).
6. How do I write the quality of the interval?
- Perfect (P): No "P" is written
- Augmented (A): Write "A" after the number (e.g., 6A)
- Diminished (D): Write "D" after the number (e.g., 2D)
7. How do I write the alteration of the interval?
- Sharp (#): Write "#" after the number (e.g., 2#)
- Flat (b): Write "b" after the number (e.g., 3b)
- Natural (n): Write "n" after the number (e.g., 5n)
8. How do I write the size of the interval?
Write the number of half steps in the interval.
9. Can I combine "A" and "D" in the same interval?
No. An interval cannot be both augmented and diminished.
10. What is an example of writing an interval in notation?
A minor third is written as "3m" (Size 3, Minor quality).