5 Easy Steps on How to Write Domain in Interval Notation: Master This Key Math Concept
Ever wondered how to write domain in interval notation? It’s a mathematical concept that describes the set of input values for which a function is defined. Don’t let the jargon scare you; writing domain in interval notation is easier than you think!
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through 5 simple steps, providing clear explanations and helpful examples. Whether you’re a student or an adult looking to brush up on your math skills, this guide will empower you to tackle this topic with confidence.
To make this learning journey even more engaging, we’ve included a featured image that visually illustrates the concept. Let’s dive right in!
Source animalia-life.club
1. Understanding Domain and Interval Notation
Before exploring how to write domain in interval notation, let’s define these terms.
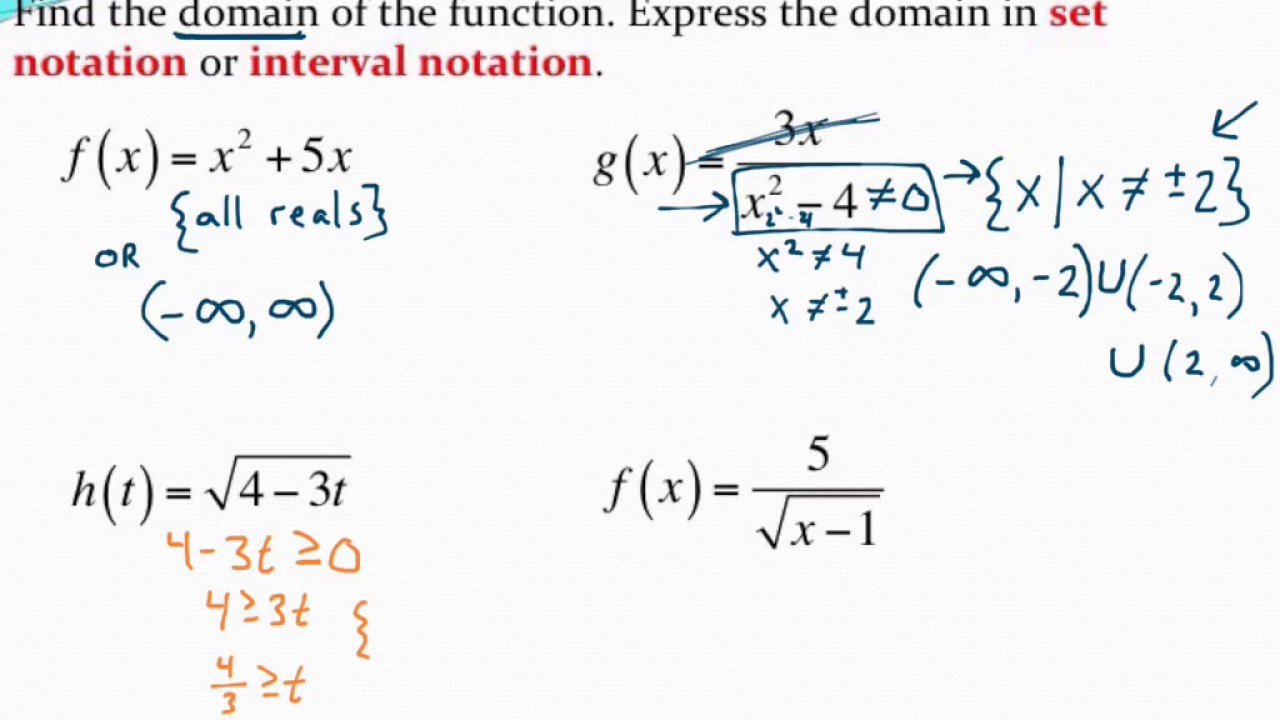
Domain: The domain of a function is the set of all possible input values for which the function is defined. In other words, it’s the range of values that can be plugged into the function without causing any mathematical errors.
Interval Notation: Interval notation is a mathematical shorthand for describing a set of real numbers. It uses symbols such as square brackets ([ ), curly brackets ({ ), and parentheses ( ) to indicate the endpoints and the type of boundary (inclusive or exclusive).
2. Step 1: Identify the Input Variable
The first step in writing domain in interval notation is to identify the input variable in the function. This is typically represented by the letter x or another variable. Identifying the input variable helps you define the range of values it can take.
3. Step 2: Determine the Lower and Upper Bounds
The next step is to determine the lower and upper bounds of the domain. These bounds represent the minimum and maximum values of the input variable for which the function is defined.
4. Step 3: Analyze the Boundaries
Once you have the lower and upper bounds, analyze the type of boundaries they are:
- Closed Boundaries (Inclusive): Represented by square brackets [a, b], which means the endpoints are included in the interval.
- Open Boundaries (Exclusive): Represented by parentheses (a, b), which means the endpoints are excluded from the interval.
- Half-Open Boundaries: A combination of open and closed boundaries, represented as [a, b) or (a, b].
5. Step 4: Write the Interval Notation
Using the information from steps 1 to 3, you can now write the domain in interval notation:
- If both bounds are closed: [lower bound, upper bound]
- If both bounds are open: (lower bound, upper bound)
- If one bound is closed and the other is open: [lower bound, upper bound) or (lower bound, upper bound]
Conclusion:
Writing domain in interval notation is a valuable skill in mathematics. By following the 5 steps outlined in this guide, you’ll be able to confidently describe the input values of a function in a concise and clear manner.
We encourage you to practice writing domain in interval notation using different functions. Remember, the key is to understand the concept and apply it correctly.
If you enjoyed this guide, please take a moment to check out our other articles on related mathematical topics. We’re committed to providing engaging and informative content that empowers you in your learning journey.
FAQ about Domain in Interval Notation
How do I write the domain of a function in interval notation?
- P: Parentheses indicate open intervals.
- A: Square brackets indicate closed intervals.
- S: Use infinity (∞) or negative infinity (-∞) for unbounded intervals.
What is an open interval?
- An interval where the endpoints are not included. Example: (0, 5)
What is a closed interval?
- An interval where the endpoints are included. Example: [0, 5]
How do I write an unbounded interval?
- Use infinity (∞) for an interval that goes to positive infinity. Example: (-∞, 5)
- Use negative infinity (-∞) for an interval that goes to negative infinity. Example: (0, ∞)
What is the domain of a constant function?
- The entire real number line, (-∞, ∞)
How do I find the domain of a piecewise function?
- State the domain for each piece separately and then combine them using set union notation (U).
What is the domain of a square root function?
- All non-negative real numbers, [0, ∞)
What is the domain of a reciprocal function?
- All real numbers except 0, (-∞, 0) U (0, ∞)
How do I write the domain of a polynomial function?
- The entire real number line, (-∞, ∞)
What is the domain of an exponential function with a positive base?
- All real numbers, (-∞, ∞)