How to Calculate Class Boundaries: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
Calculating class boundaries is a fundamental step in data analysis and statistics. It helps you organize and represent your data effectively, making it easier to draw meaningful insights. This guide will take you through the process step-by-step, ensuring you can tackle this task confidently.

Source tomawarner.blogspot.com
Source tomawarner.blogspot.com
1. Understanding Class Boundaries
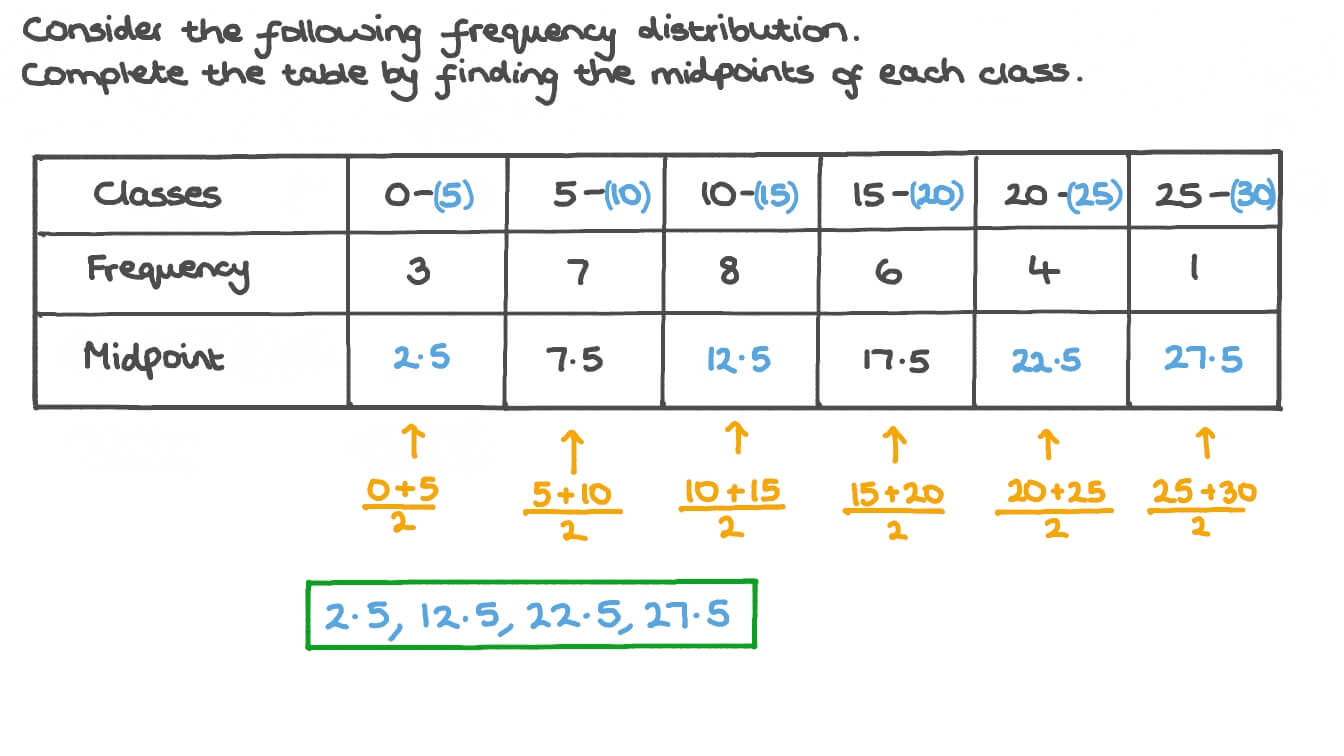
Simply put, class boundaries are the points that divide your data into equal-sized groups called classes. These boundaries help you represent the distribution of your data in a structured manner.
2. Determining the Number of Classes
The first step is deciding how many classes you want to create. This decision depends on the nature of your data and the level of detail you need. A good rule of thumb is to aim for around 5-10 classes to balance clarity and detail.
3. Calculating Class Width
The class width represents the range covered by each class. To calculate it, subtract the minimum value from the maximum value in your data and divide that difference by the number of classes.
Class Width = (Maximum Value - Minimum Value) / Number of Classes
4. Setting the Class Boundaries
Now it’s time to set the actual class boundaries. Start by adding the class width to the minimum value. Repeat this process to get the subsequent boundaries until you reach the maximum value.
First Boundary = Minimum Value
Subsequent Boundaries = First Boundary + Class Width
5. Assigning Data to Classes
With the boundaries set, you can assign each data point to its corresponding class. Data points that fall within the first boundary belong to the first class, data points within the second boundary belong to the second class, and so on.
6. Representing the Data
Finally, you can represent your data using the class boundaries and frequency counts. A frequency count indicates how many data points belong to each class. This can be done using a bar chart or a histogram.
Conclusion
Calculating class boundaries is a valuable skill that allows you to organize and visualize your data effectively. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can confidently carry out this task and unlock the insights hidden within your data.
Stay tuned for other informative articles on data analysis and statistics. We’ll help you become a data-savvy pro in no time!
FAQ about Class Boundaries
What are class boundaries?
Answer: Class boundaries are the dividing points between classes in a frequency distribution.
How do I calculate the lower class boundary?
Answer: Subtract 0.5 from the lower limit of the class.
How do I calculate the upper class boundary?
Answer: Add 0.5 to the upper limit of the class.
What is the purpose of class boundaries?
Answer: Class boundaries help to ensure that data points are assigned to the correct class.
How do I calculate the width of a class interval?
Answer: Subtract the lower class boundary from the upper class boundary.
What is the difference between a class interval and a class boundary?
Answer: A class interval is the range of values included in a class, while a class boundary is the dividing point between two classes.
How do I determine the number of classes?
Answer: There is no set rule, but a good rule of thumb is to use between 5 and 15 classes.
What is Sturges’ rule?
Answer: Sturges’ rule is a formula for determining the number of classes: k = 1 + 3.3 log n, where n is the number of data points.
What is the Sheppard’s correction?
Answer: Sheppard’s correction is a method for adjusting the class boundaries to account for the fact that data points are not always evenly distributed within a class.
What is the added-width correction?
Answer: The added-width correction is a method for adjusting the class boundaries to account for the fact that the width of the first and last class intervals is different from the width of the other class intervals.