How to Find Frequency Distribution: A Step-by-Step Guide
Are you grappling with understanding data and uncovering patterns within it? If so, frequency distribution can be your guiding light! Join us on a journey to demystify this essential statistical concept and empower you with the knowledge to decipher data like a pro.
What is Frequency Distribution?
Frequency distribution is a statistical tool that helps us organize and understand the occurrence of different values in a dataset. It paints a picture of how frequently each value appears, revealing patterns and trends within the data.
Source brokeasshome.com
Imagine a survey asking respondents about their favorite ice cream flavors. By organizing the responses into a frequency distribution, we can quickly identify the most popular and least popular flavors, gaining valuable insights into consumer preferences.
Why is Frequency Distribution Important?
Frequency distribution is a cornerstone of data analysis, providing several key benefits:
- Identifying Trends: It reveals the most and least frequently occurring values, helping identify trends and patterns in the data.
- Data Summarization: It condenses large datasets into manageable summaries, making it easier to comprehend and communicate data insights.
- Hypothesis Testing: Frequency distribution can be used as a foundation for hypothesis testing, allowing us to test assumptions about the underlying distribution of values.
How to Find Frequency Distribution: A Step-by-Step Guide
Finding frequency distribution is as easy as 1-2-3! Follow these steps and you’ll be a frequency distribution maestro in no time:
1. Sort Your Data
Arrange your data in ascending or descending order to create a more organized dataset. This will make it easier to identify duplicate values and count their occurrences.
2. Count the Occurrences
For each value in your sorted dataset, count how many times it appears. These counts represent the frequency of each value.
3. Create a Frequency Table
Construct a table with two columns: one for the values and another for their corresponding frequencies. This table will provide a clear overview of the frequency distribution.
Example: Calculating Frequency Distribution
Let’s say we have the following data set:
{10, 15, 10, 12, 15, 18, 10, 12, 18, 15}
Step 1: Sort the data
{10, 10, 10, 12, 12, 15, 15, 15, 18, 18}
Step 2: Count the occurrences
| Value | Frequency |
|---|---|
| 10 | 3 |
| 12 | 2 |
| 15 | 3 |
| 18 | 2 |
Step 3: Create a frequency table
| Value | Frequency |
|---|---|
| 10 | 3 |
| 12 | 2 |
| 15 | 3 |
| 18 | 2 |
Comparison of Frequency Distribution Methods
Choosing the right frequency distribution method depends on the nature of your data. Here’s a comparison to help you make an informed decision:
| Method | Purpose | Suitable for |
|---|---|---|
| Ungrouped Frequency Distribution | Detailed analysis of individual values | Small datasets or qualitative data with few categories |
| Grouped Frequency Distribution | Summarization of data for large datasets | Data with a wide range of values or continuous variables |
| Cumulative Frequency Distribution | Cumulative representation of data | Identifying percentiles or quantiles |
Conclusion
Unlocking the power of frequency distribution is now within your reach! By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can transform raw data into meaningful insights, uncover trends, and draw informed conclusions.
Remember, frequency distribution is a valuable tool in your statistical toolkit. Embrace its potential and it will empower you to make sense of data and make informed decisions.
Don’t stop here! Explore other articles on our blog to further expand your data analysis skills. Let’s dive deeper into the fascinating world of statistics together!
FAQ about Finding Frequency Distribution
What is frequency distribution?
Answer: Frequency distribution is a statistical technique used to organize data into groups based on their frequency or how often they occur.
How do I find the frequency distribution of a dataset?
Answer: To find the frequency distribution, group the data into equal intervals called classes, then count the number of data points that fall into each class.
What is the formula for frequency distribution?
Answer: Frequency (f) = Number of data points in each class / Total number of data points
What is the difference between grouped and ungrouped frequency distribution?
Answer: Grouped frequency distribution groups data into classes, while ungrouped frequency distribution presents the data in its original form without grouping.
How do I determine the class width?
Answer: Class width is the difference between the upper and lower limits of each class. It is calculated by dividing the range (highest value – lowest value) of the dataset by the desired number of classes.
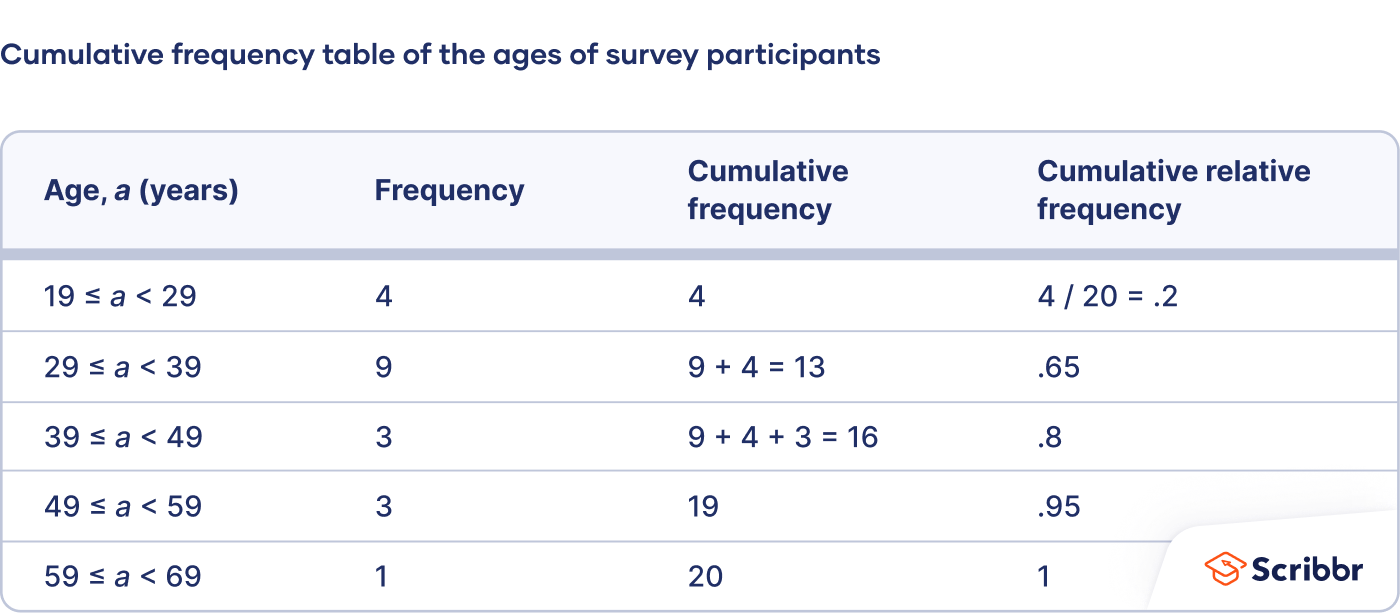
What is the cumulative frequency distribution?
Answer: Cumulative frequency distribution calculates the running total of frequencies up to each class. It helps identify the percentage of data that falls below or above a particular value.
How do I create a frequency distribution table?
Answer: Create a table with columns for class intervals, frequencies, and cumulative frequencies. Fill in the appropriate values for each class.
How do I represent a frequency distribution graphically?
Answer: You can represent it using a histogram, bar graph, or frequency polygon. Each bar or point on the graph represents the frequency of data within that class.
What is the purpose of finding frequency distribution?
Answer: Frequency distribution helps summarize data, identify patterns, make inferences, and compare different datasets.
How do I interpret a frequency distribution?
Answer: Analyze the distribution to identify the most frequent values, the range of values, the skewness or symmetry of the distribution, and any outliers.