How to Find the Instantaneous Rate of Change: A Step-by-Step Guide
Do you want to measure how fast a function is changing at a particular moment? If so, then you need to find its instantaneous rate of change, also known as the derivative! This guide will show you everything you need to know about finding the instantaneous rate of change, with clear examples and step-by-step instructions. 😊👍
Source collegedunia.com
What is the Instantaneous Rate of Change?
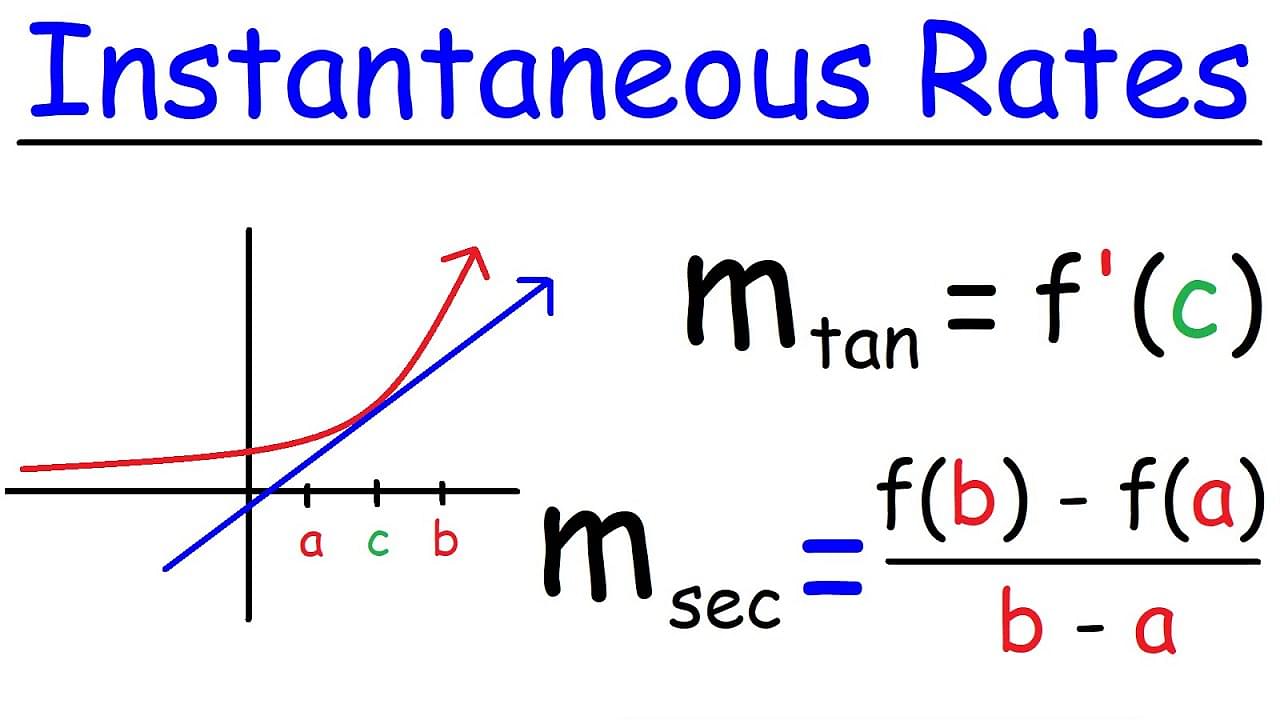
The instantaneous rate of change measures how quickly a function is changing at a specific point in time. It’s the slope of the tangent line to the graph of the function at that point. This means that it tells you the direction and steepness of the curve at that moment.
How to Find the Instantaneous Rate of Change
There are two main ways to find the instantaneous rate of change:
1. Using the Definition
The definition of the instantaneous rate of change is:
f'(x) = lim (h->0) [f(x + h) - f(x)] / h
where:
- f(x) is the function
- f'(x) is the derivative of f(x)
- h is a small change in x
2. Using a Difference Quotient
A difference quotient is a simplified version of the definition that can be used to find the instantaneous rate of change:
f'(x) = [f(x + h) - f(x)] / h
where:
- f(x) is the function
- h is a small change in x
Step-by-Step Instructions
Using the Definition
- Start with the definition: f'(x) = lim (h->0) [f(x + h) – f(x)] / h
- Substitute the function f(x) into the definition.
- Simplify the expression as much as possible.
- Take the limit as h approaches 0.
Using a Difference Quotient
- Start with the difference quotient: f'(x) = [f(x + h) – f(x)] / h
- Substitute a small value of h into the difference quotient (such as h = 0.001).
- Simplify the expression as much as possible.
- Evaluate the expression for the given value of x.
Examples
Example 1: Using the Definition
Find the instantaneous rate of change of the function f(x) = x^2 at x = 2.
- f'(x) = lim (h->0) [f(2 + h) – f(2)] / h
- f'(x) = lim (h->0) [(2 + h)^2 – 2^2] / h
- f'(x) = lim (h->0) [4 + 4h + h^2 – 4] / h
- f'(x) = lim (h->0) [4h + h^2] / h
- f'(x) = lim (h->0) [h(4 + h)] / h
- f'(x) = lim (h->0) 4 + h
- f'(x) = 4
Example 2: Using a Difference Quotient
Find the instantaneous rate of change of the function f(x) = sin(x) at x = π/2.
- f'(x) = [f(π/2 + h) – f(π/2)] / h
- f'(x) = [sin(π/2 + h) – sin(π/2)] / h
- f'(x) = [cos(h) – 1] / h
- f'(x) = cos(π/2 + h) / h – 1 / h
- f'(x) = 0 / h – 1 / h
- f'(x) = -1 / h
- f'(π/2) = -1 / 0.001 = -1000
Interpreting the Instantaneous Rate of Change
Once you have found the instantaneous rate of change, you can interpret it to understand the behavior of the function at that point. A positive instantaneous rate of change indicates that the function is increasing at that point, while a negative instantaneous rate of change indicates that the function is decreasing at that point. The magnitude of the instantaneous rate of change tells you how quickly the function is changing.
Comparison Table
| Method | Definition | Difference Quotient |
|---|---|---|
| Formula | f'(x) = lim (h->0) [f(x + h) – f(x)] / h | f'(x) = [f(x + h) – f(x)] / h |
| Accuracy | More accurate | Less accurate |
| Difficulty | More difficult | Easier |
Conclusion
Now you know how to find the instantaneous rate of change! Use this powerful tool to analyze functions and understand their behavior.
If you want to learn more about calculus, check out our other articles on derivatives, integrals, and limits. 😊👍
FAQ about Instantaneous Rate of Change
What is the instantaneous rate of change?
- Answer: The instantaneous rate of change is the slope of the tangent line to a curve at a given point. It represents the rate at which the dependent variable changes with respect to the independent variable at that specific instant.
How do I find the instantaneous rate of change?
- Answer: To find the instantaneous rate of change, you can use the following steps:
- Find the derivative of the function with respect to the independent variable.
- Evaluate the derivative at the given value of the independent variable.
What is the formula for the instantaneous rate of change?
- Answer: The formula for the instantaneous rate of change is:
- dy/dx = lim (Δy/Δx) as Δx approaches 0
What is the difference between the instantaneous rate of change and the average rate of change?
- Answer: The instantaneous rate of change measures the rate of change at a specific point in time, while the average rate of change measures the rate of change over a given interval.
How do I use the instantaneous rate of change to understand a graph?
- Answer: The instantaneous rate of change can be used to determine the slope of the tangent line to a graph at any given point. This information can be used to analyze the behavior of the function and to identify critical points.
What are some applications of the instantaneous rate of change?
- Answer: The instantaneous rate of change has applications in various fields, including:
- Physics (velocity and acceleration)
- Economics (marginal cost and marginal revenue)
- Biology (population growth and decay)
How can I find the equation of the tangent line using the instantaneous rate of change?
- Answer: To find the equation of the tangent line using the instantaneous rate of change, you can use the following steps:
- Find the instantaneous rate of change at the given point.
- Use the point-slope form of a linear equation: y – y1 = m(x – x1), where (x1, y1) is the given point and m is the instantaneous rate of change.
What is the relationship between the instantaneous rate of change and the derivative?
- Answer: The instantaneous rate of change is equal to the derivative of the function with respect to the independent variable.
How do I find the instantaneous rate of change of a function that is not differentiable?
- Answer: If a function is not differentiable, you cannot find the instantaneous rate of change using the usual methods. However, you can use numerical methods, such as the finite difference method, to approximate the instantaneous rate of change.
What is the significance of the instantaneous rate of change being zero?
- Answer: If the instantaneous rate of change of a function is zero at a given point, it means that the function is not changing at that point. This can indicate a maximum, a minimum, or a point of inflection.