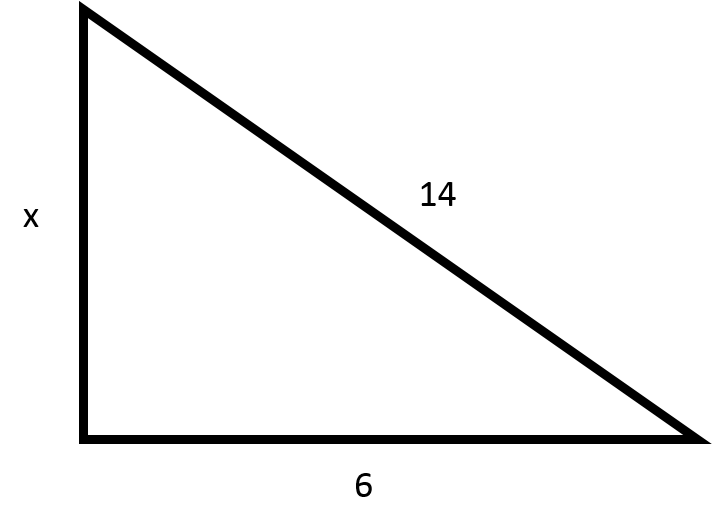
3 Easy Ways to Find the Missing Length of a Right Triangle
Are you puzzling over how to find the missing length of a right triangle? Don’t fret, because we’re here to guide you through it with three simple yet powerful methods. Whether you’re a student looking to ace your geometry exam or a DIY enthusiast tackling a project, these techniques will empower you to conquer this math challenge.
Source uiplynejef.blogspot.com
Method 1: Pythagorean Theorem
The legendary Pythagorean Theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (the longest side) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides:
a² + b² = c²
Where:
aandbare the lengths of the two shorter sides (legs)cis the length of the hypotenuse
To find the missing length, simply rearrange the formula to solve for the unknown side:
- If you know
aandb, solve forc:c = √(a² + b²). - If you know
canda, solve forb:b = √(c² - a²). - If you know
candb, solve fora:a = √(c² - b²).
Method 2: Special Right Triangles
Certain right triangles have specific ratios between their side lengths. These are known as special right triangles. By memorizing these ratios, you can quickly find the missing length without using the Pythagorean Theorem.
- 45-45-90 Triangle: Sides are in a ratio of 1:1:√2.
- 30-60-90 Triangle: Sides are in a ratio of 1:√3:2.
Simply multiply the known side length by the appropriate ratio to find the missing length.
Method 3: Trigonometry
Trigonometry is the branch of mathematics that deals with relationships between the sides and angles of triangles. In a right triangle, where one angle is 90°, we can use the trigonometric ratios of sine, cosine, and tangent to find the missing length.
- Sine (sin): Opposite side / Hypotenuse
- Cosine (cos): Adjacent side / Hypotenuse
- Tangent (tan): Opposite side / Adjacent side
To find the missing length, rearrange the trigonometric ratio to solve for the unknown side. For example, if you know the angle and the length of one side:
- If you know the angle and the length of the opposite side, solve for the hypotenuse:
c = opposite side / sin(angle). - If you know the angle and the length of the adjacent side, solve for the hypotenuse:
c = adjacent side / cos(angle). - If you know the angle and the length of the opposite side, solve for the adjacent side:
adjacent side = opposite side / tan(angle).
Comparison Table:
| Method | Formula | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pythagorean Theorem | a² + b² = c² |
Easy to understand | Requires knowing two side lengths |
| Special Right Triangles | Memorize ratios | Quick and easy for specific triangles | Only works for special triangles |
| Trigonometry | Trigonometric ratios (sin, cos, tan) | Can find missing length from any angle and side | Requires understanding of trigonometry |
Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve now mastered three powerful methods to find the missing length of a right triangle. Whether you’re tackling a geometry problem or planning a home improvement project, these techniques will empower you to solve your triangle conundrums. Don’t hesitate to explore our other articles for more math tips and tricks.
FAQ about Triangles
1. How do I find the missing length of a right triangle when I have the other two lengths?
Answer: By using the Pythagorean Theorem: a^2 + b^2 = c^2, where a and b are the lengths of the two known sides, and c is the length of the missing side (the hypotenuse).
2. What if only the sum of the squares of the two known lengths is given?
Answer: Multiply the sum by 2 and then take the square root of the result.
3. Is there a way to find the missing length without the Pythagorean Theorem?
Answer: Yes, by using the trigonometric functions sine, cosine, and tangent. If you know the length of a side and the measure of an angle, you can find the length of the missing side.
4. What if I only know the area of the triangle and one length?
Answer: Use the formula A = (1/2) * b * h, where A is the area, b is the length of the known side, and h is the missing length. Rearrange the formula to solve for h.
5. What is the difference between the hypotenuse and the other two sides?
Answer: The hypotenuse is the longest side and is opposite the right angle. The other two sides are called the legs.
6. Can I use trigonometry to find the missing length of a triangle that is not a right triangle?
Answer: Yes, but the process is more complex and involves using the Law of Cosines.
7. How do I know which side is the hypotenuse?
Answer: The hypotenuse is always opposite the right angle.
8. Are there any special cases where the missing length can be easily found?
Answer: Yes, if the triangle is a 3-4-5 right triangle (Pythagorean triple).
9. Can I use a scientific calculator to find the missing length?
Answer: Yes, the calculator can perform the necessary calculations using the Pythagorean Theorem or trigonometric functions.
10. Is it possible to have a right triangle with irrational side lengths?
Answer: Yes, for example, a triangle with side lengths of √2, √2, and 2.