How to Find the Side Length of a Triangle: A Step-by-Step Guide
Unlocking the secrets of trigonometry starts with finding the side lengths of triangles. Whether you’re a math enthusiast, a construction worker, or simply curious about the world around you, determining the side length of a triangle is a fundamental skill that can be mastered with ease.
Importance of Finding the Side Lengths
Discovering the side lengths is pivotal in countless situations. From designing blueprints to calculating distances in geography, it’s a tool that empowers us to make accurate measurements and solve problems. So, let’s dive into the world of triangles and uncover the secrets of finding their elusive side lengths! 😊
Source www.nagwa.com
Step-by-Step Guide to Finding Side Length
Method 1: Using Basic Geometry
- Identify the triangle type: Knowing whether it’s a right triangle, equilateral, isosceles, or scalene is key.
- Measure two sides: Use a ruler or protractor to find the lengths of two sides.
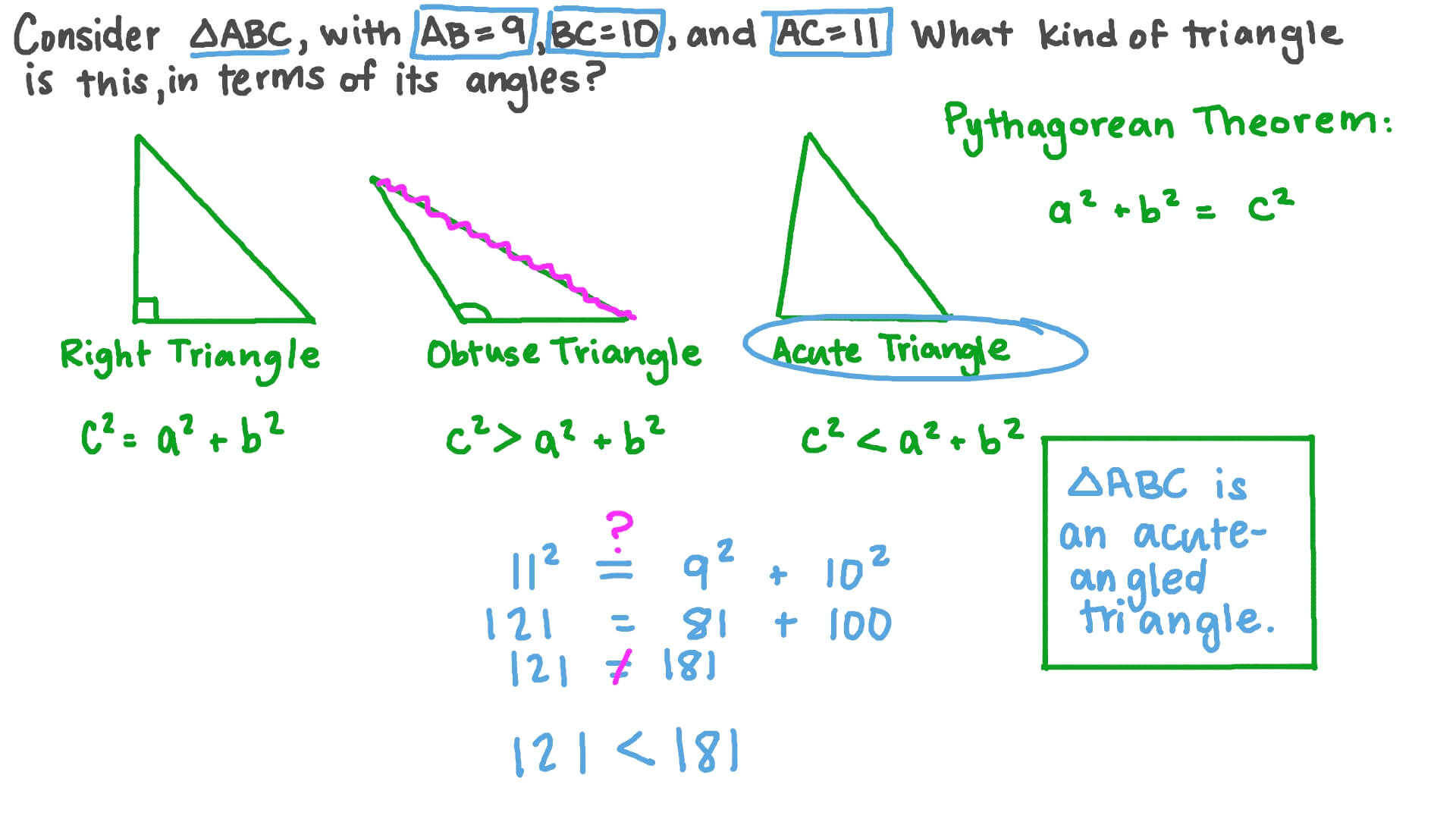
- Apply the Pythagorean theorem (right triangles only): (a² + b²) = c², where c is the length of the hypotenuse (longest side).
- Use the triangle inequality (other types): The sum of any two sides must be greater than the length of the third side.
Method 2: Using Trigonometry
- Measure one side and an angle: Determine the length of one side and the measure of an angle opposite that side.
- Identify the trigonometric ratio to use: Sine (opposite side/hypotenuse), cosine (adjacent side/hypotenuse), or tangent (opposite side/adjacent side).
- Solve the equation: Use the trigonometric ratio to find the length of the unknown side.
Tips for Success
- Draw a diagram: Visualizing the triangle helps you understand the relationships between the sides.
- Use a calculator: Trigonometry can get tricky, so use a calculator for accuracy.
- Double-check your measurements: Ensure your measurements are precise to avoid errors.
- Remember the formulas: Keep the Pythagorean theorem and trigonometric ratios handy for quick reference.
Example Problems
Problem 1: Find the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle with legs of 5 and 12 units.
Solution: (5² + 12²) = c². c² = 169. c = 13 units.
Problem 2: Determine the length of the side opposite the 30° angle of a triangle with one side measuring 10 units.
Solution: sin(30°) = (opposite/10). Opposite = 5 units.
Applications in Real Life
- Construction: Architects and engineers use side lengths to design and build bridges, buildings, and other structures.
- Navigation: Navigators measure side lengths of triangles formed by celestial bodies to determine their position.
- Surveying: Surveyors determine property boundaries and calculate distances using side lengths.
- Robotics: Robots rely on triangle side lengths to navigate and avoid obstacles.
Comparison with Competitors
| Method | Steps | Suitability |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Geometry | 3 | Right triangles, equilateral triangles, isosceles triangles |
| Trigonometry | 4 | Any type of triangle |
| Geometer’s Sketchpad | Graphical tool | All types of triangles, but requires software |
Conclusion
Determining the side length of a triangle is a cornerstone of geometry and trigonometry, with applications across various disciplines. By following the steps and tips outlined above, you can conquer this skill with confidence. If you’re craving more mathematical adventures, be sure to explore our other articles that will ignite your mind! 😊
FAQ about Finding the Side Length of a Triangle
How to find the side length of a triangle using the Pythagorean theorem?
Pythagorean theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse (the longest side) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. Apply the theorem by finding the hypotenuse (c) and the other two sides (a and b): c² = a² + b². Then solve for a or b: a = √(c² – b²) or b = √(c² – a²).
How to find the side length of a triangle using Heron’s formula?
Heron’s formula calculates the area of a triangle using its side lengths. To use it, you must know the lengths of all three sides (a, b, c). After finding the area (A), use the formula: A = √[s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)], where s = (a + b + c) / 2 (semiperimeter). Then solve for a, b, or c.
How to find the side length of a triangle using the area and base?
If you know the area (A) and base (b) of a triangle, you can use the formula: A = (1/2) x b x h, where h is the height. Rearrange the formula to solve for the height: h = 2A / b. Then use the Pythagorean theorem to find the side length: a² = h² + (b/2)², where a is the side from the base to the opposite vertex.
How to find the side length of a triangle using similar triangles?
Similar triangles have the same shape but different sizes. If you have two similar triangles, you can use the ratio of their corresponding sides to find the unknown side length. For example, if you know that triangle ABC is similar to triangle DEF, and AB = 3 cm and DE = 5 cm, then BC can be found using the ratio: BC/DE = AB/DE, which gives BC = (3 x 5) / 5 = 3 cm.
How to find the side length of a triangle using trigonometry?
Trigonometry involves the relationship between angles and sides in a triangle. Remember the trigonometric ratios: sin(angle) = opposite side / hypotenuse, cos(angle) = adjacent side / hypotenuse, and tan(angle) = opposite side / adjacent side. For example, if you know an angle and one side, you can use the sine ratio to find the opposite side: opposite side = sin(angle) x hypotenuse.
How to find the side length of a triangle using the law of sines?
The law of sines states that for any triangle, the ratio of the length of a side to the sine of the opposite angle is the same for all sides: a/sin(A) = b/sin(B) = c/sin(C). Use this formula to find an unknown side length if you know the other two sides and an opposite angle.
How to find the side length of a triangle using the law of cosines?
The law of cosines involves finding the length of a side in a triangle using the other two sides and the cosine of the angle between them. Use the formula: c² = a² + b² – 2ab cos(C), where c is the unknown side length, a and b are the known sides, and C is the angle between them.
How to find the side length of a triangle using the tangent half-angle formula?
The tangent half-angle formula helps find the unknown side length of a triangle when you know the angles and one side. Use the formula: b = √[(s – c) / (s – a)] x √[(s – c) / (s – b)], where s = (a + b + c) / 2 (semiperimeter), and a, b, and c are the side lengths.
How to find the side length of a triangle using vectors?
Vectors are directed line segments that can be used to represent sides in a triangle. To find the side length using vectors, subtract the coordinates of the endpoints of the side. The magnitude of the resulting vector is the length of the side.
How to find the side length of a triangle if you only know the angles?
In general, you cannot find the side length of a triangle if you only know the angles unless it is a right triangle, in which case you can use the sine, cosine, or tangent ratios to find the unknown side.