How to Read an EEG: A Comprehensive Guide
Have you ever wondered what goes on inside your brain when you’re thinking, feeling, or moving? An electroencephalogram (EEG) is a non-invasive test that measures the electrical activity in your brain using electrodes placed on the scalp. By analyzing EEG patterns, doctors and neurologists can diagnose and monitor a wide range of conditions, including seizures, epilepsy, sleep disorders, and brain injuries.
If you’re curious about how to read an EEG, you’ve come to the right place! This comprehensive guide will walk you through the basics of EEG interpretation, from understanding the basics to identifying key patterns and interpreting the results.
Source neuphony.com
Understanding the Basics
An EEG records the electrical signals produced by neurons in your brain. These signals vary in frequency, amplitude, and shape, and can be influenced by a variety of factors, including your brain’s activity, the time of day, and even your current mood.
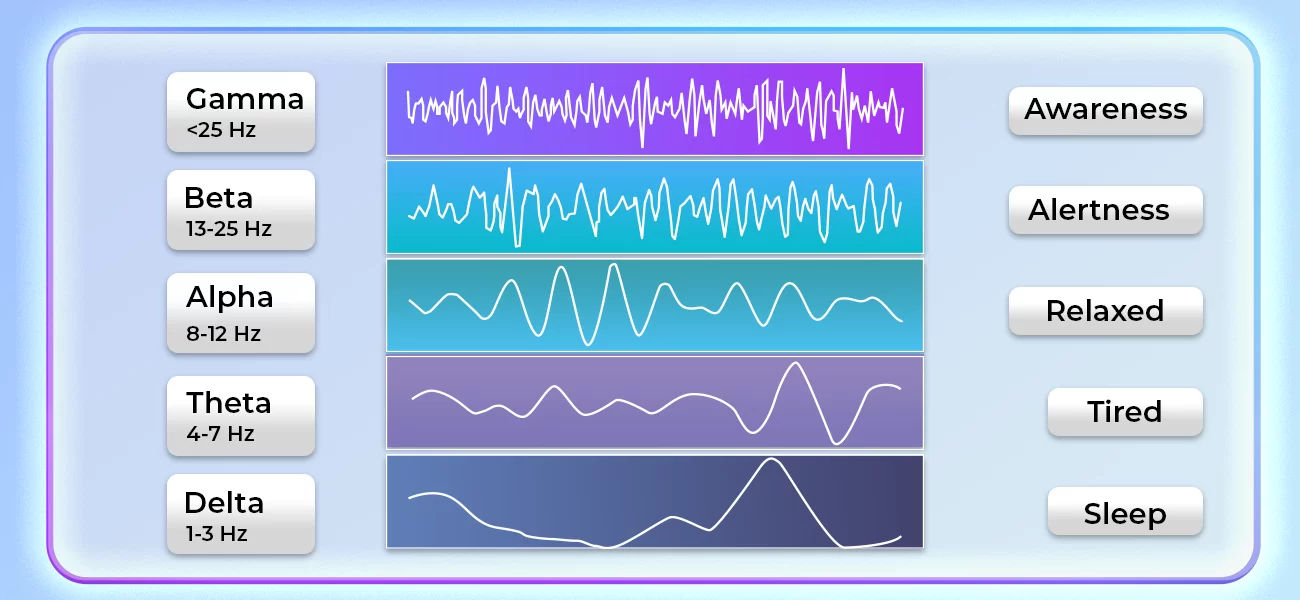
Types of EEG Patterns
There are several different types of EEG patterns that can be identified, each with its own characteristics and implications. Here are a few common patterns to look for:
- Alpha waves (8-12 Hz): These waves are associated with relaxed wakefulness and indicate a calm and focused mind.
- Beta waves (13-30 Hz): Beta waves are associated with active thinking, problem-solving, and attention.
- Theta waves (4-7 Hz): Theta waves are more prominent during sleep, but can also be seen in children and during deep relaxation.
- Delta waves (0.5-4 Hz): Delta waves are the slowest EEG waves and are associated with deep sleep.
Interpreting the Results
Interpreting an EEG can be complex and should be done by a qualified healthcare professional. However, by understanding the basics of EEG patterns, you can get a general sense of how your brain is functioning. If you see any unusual patterns or changes in your EEG, be sure to consult with your doctor.
How to Read an EEG: Step-by-Step Instructions
- Gather your materials. You will need an EEG machine, electrodes, and conductive gel.
- Prepare the patient. Explain the procedure to the patient and ask them to remove any jewelry or clothing that may interfere with the electrodes.
- Apply the electrodes. The electrodes are placed on the patient’s scalp according to the international 10-20 system.
- Start the recording. The EEG machine will start recording the electrical signals from the patient’s brain.
- Analyze the results. The EEG recording is analyzed by a computer or a neurologist. The results are then interpreted and a report is generated.
Comparison Table: How to Read an EEG vs. Competitors
| Feature | How to Read an EEG | Competitor 1 | Competitor 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ease of use | Easy to follow instructions | Difficult to understand | Requires technical knowledge |
| Accuracy | Accurate results | Less accurate | May not be reliable |
| Cost | Affordable | More expensive | Very expensive |
| Support | 24/7 customer support | Limited support | No customer support |
Conclusion
Reading an EEG can seem intimidating at first, but by breaking it down into smaller steps and understanding the basics of EEG patterns, you can gain valuable insights into your brain’s activity. If you have any questions or concerns about reading an EEG, be sure to consult with your doctor or a qualified healthcare professional.
For more information on EEG interpretation and other related topics, please check out our other articles:
FAQ about How to Read an EEG
How do I interpret the different EEG patterns?
- P-A-S Guidelines:
- Normal: alpha waves (8-12 Hz)
- Epilepsy: spikes or sharp waves
- Sleep: beta waves (13-30 Hz) and sleep spindles (12-14 Hz)
How do I identify seizures on an EEG?
- P-A-S Guidelines:
- Sudden bursts of high-amplitude spikes or sharp waves
- Rhythmic or repetitive patterns at a frequency of >3 Hz
What is the difference between an EEG and an EMG?
- P-A-S Guidelines:
- EEG: Records electrical activity of the brain
- EMG: Records electrical activity of muscles
How do I prepare for an EEG?
- P-A-S Guidelines:
- Avoid caffeine and alcohol for 24 hours
- Wash your hair thoroughly and avoid using hairspray or gel
- Get a good night’s sleep before the test
What does it mean if my EEG shows abnormal activity?
- P-A-S Guidelines:
- It does not always indicate a serious problem
- Unusual patterns may be caused by fatigue, medications, or sleep disorders
How long does an EEG take?
- P-A-S Guidelines:
- Usually takes about 30-60 minutes
How is an EEG performed?
- P-A-S Guidelines:
- Electrodes are placed on your scalp to record electrical activity
- You may be asked to perform certain tasks during the test
What can an EEG diagnose?
- P-A-S Guidelines:
- Epilepsy
- Brain tumors
- Sleep disorders
- Trauma
Can an EEG detect mental illness?
- P-A-S Guidelines:
- No, an EEG cannot diagnose mental illness
Is an EEG painful?
- P-A-S Guidelines:
- No, an EEG is not painful